Binary Search Tree
- An ordered binary tree
- For every node, all elements in its left subtree are less and any elements in its right subtree are greater
- Used because they can quickly search and sort
- Height (N is number of nodes)
- Average:
- Worst case:
Terminology
- Predecessor: Left subtree’s rightmost node
- Successor: Right subtree’s leftmost node-
Operations
| Operation | Best Case | Worst Case |
|---|---|---|
| Searching | ||
| Insertion | ||
| Deletion |
Searching
search(target, root)
if the tree is empty
return null
else if target == root.data
return root.data
else if target < root.data
return seach(root.left)
else
return search(root.right)Time complexity:
- Worst case: (when tree is basically a linked list)
- Average case:
Insertion
TreeNode insert(item, root)
if root == null
return TreeNode(item)
else if item < root.data
root.left = insert(item, root.left)
else
root.right = insert(item, root.right)
return rootDeletion
delete(item, root)
if root == null
// item is not in tree
return null
if item < root.data
root.left = delete(item, root.left)
else if item > root.data
root.right = delete(item, root.right)
else //the item is in the local root
if root has no children
delete root
return null
else if root has one child
child = root.child // the one that exists
delete root
return child
else // replace with inorder successor
successor = getMinimum(curr->right);
val = successor.val
delete(val, root) // delete successor
root.val = val
return rootTraversal
- Iterating over a tree such that you touch every node
- Two strategies
- Depth First: Goes down an entire branch
- Breadth First: Goes through and entire level
Depth First
traverse(root)
if root == null
return
else
// order changes depending on type of traveral
traverse(root.left) // L
visit root // N
traverse(root.right) // R- Uses a stack (through recursion typically)
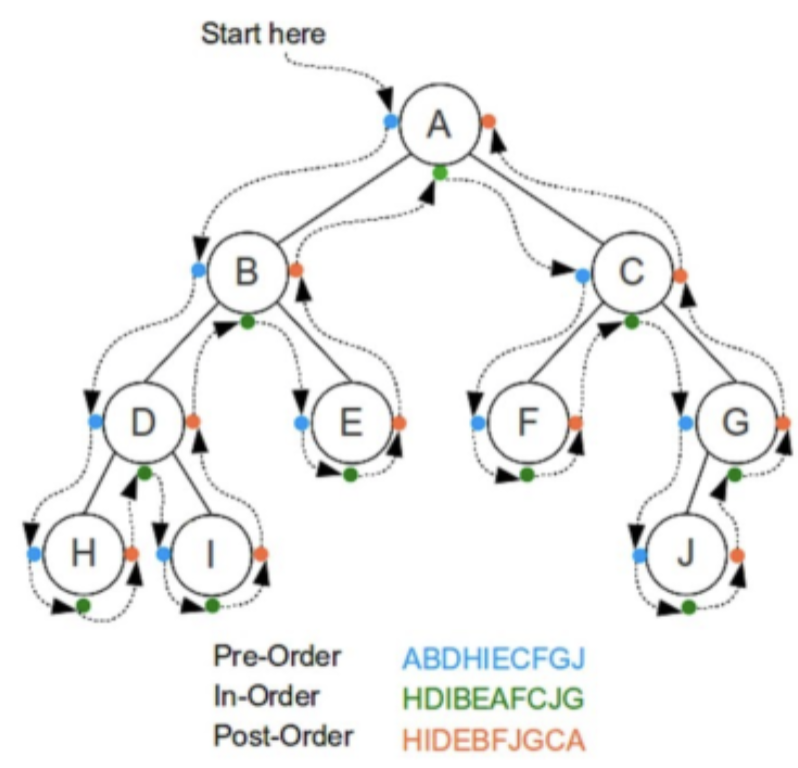
- Inorder
- Order: LNR
- Uses
- Returns the sequence in ascending order
- Is able to get a sorted list in O(n)
- Preorder
- Order: NLR
- Work at a node is done before (pre) its children
- Uses
- Printing dictionary listing
- Making a copy of a tree
- The true depth first search (goes down an entire branch at a time)
- Postorder
- Order: LRN
- Work at a node is done after (post) its children
- Uses
- Deallocating every node in a tree
- Calculating an accumulated sum for each node and all descendants
- Strategy for quickly reading
Breadth First
- AKA Level Order
- Types
- Spiral approach (always L→R or R→L)
- Zig Zag approach (alternates direction for each line)
- Uses a queue
- “Queue… I’m out of breadth”
void levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root != nullptr) {
q.push(root);
}
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front();
if (q.front()->left != nullptr)
q.push(q.front()->left);
if (q.front()->right != nullptr)
q.push(q.front()->right);
q.pop();
}
}