Control
- Part of the processor
- read instructions from memory
- issue signals to control the information flow between the datapath components and what operations t hey perform
- tells the datapath, memory, and I/O devices what to do instructions of the program
Control Signals
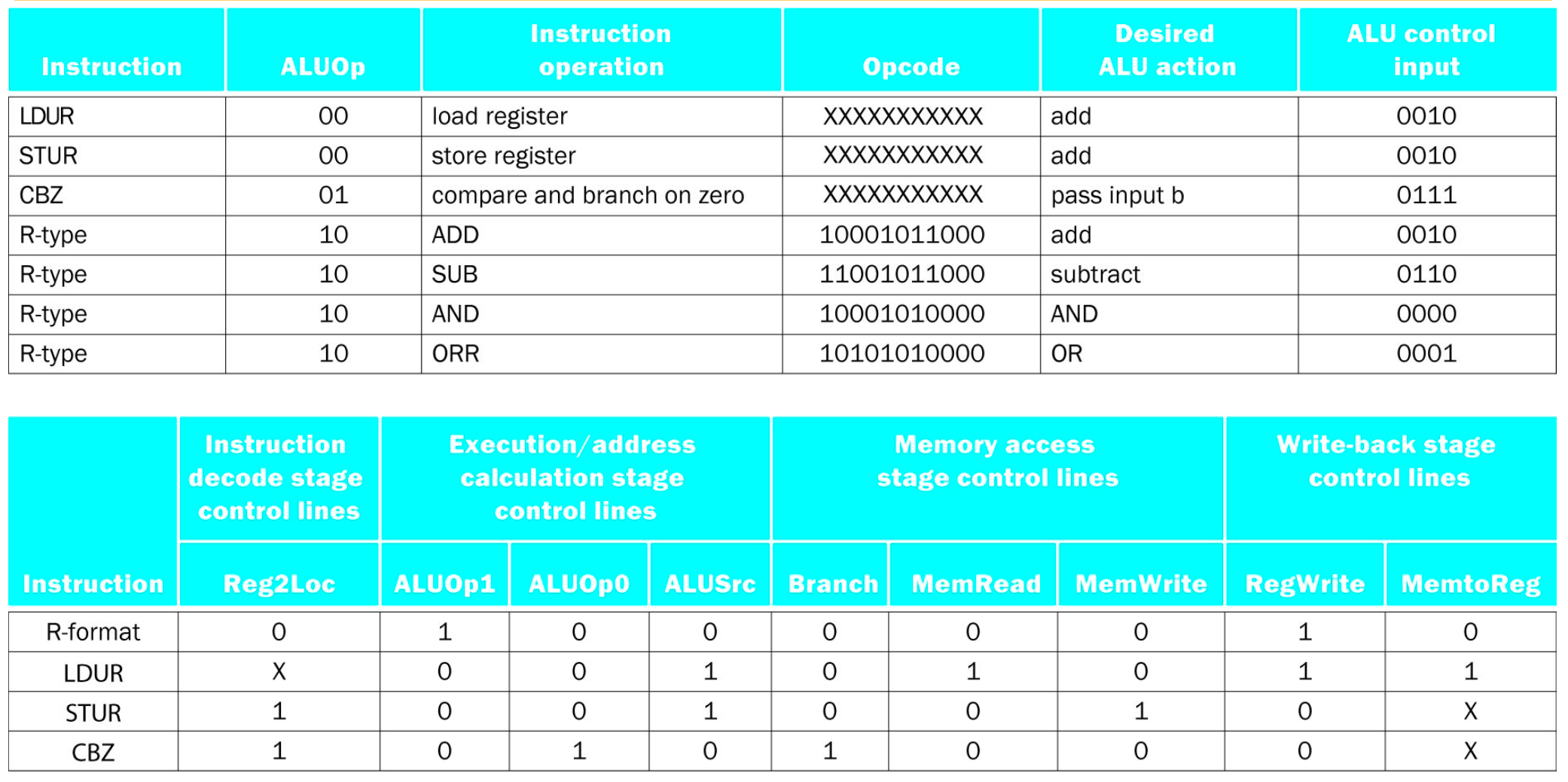
ALU Control
- Takes the instruction and finds what OPCode to feed into the ALU to do the instruction
With Pipelining
- Pipelining
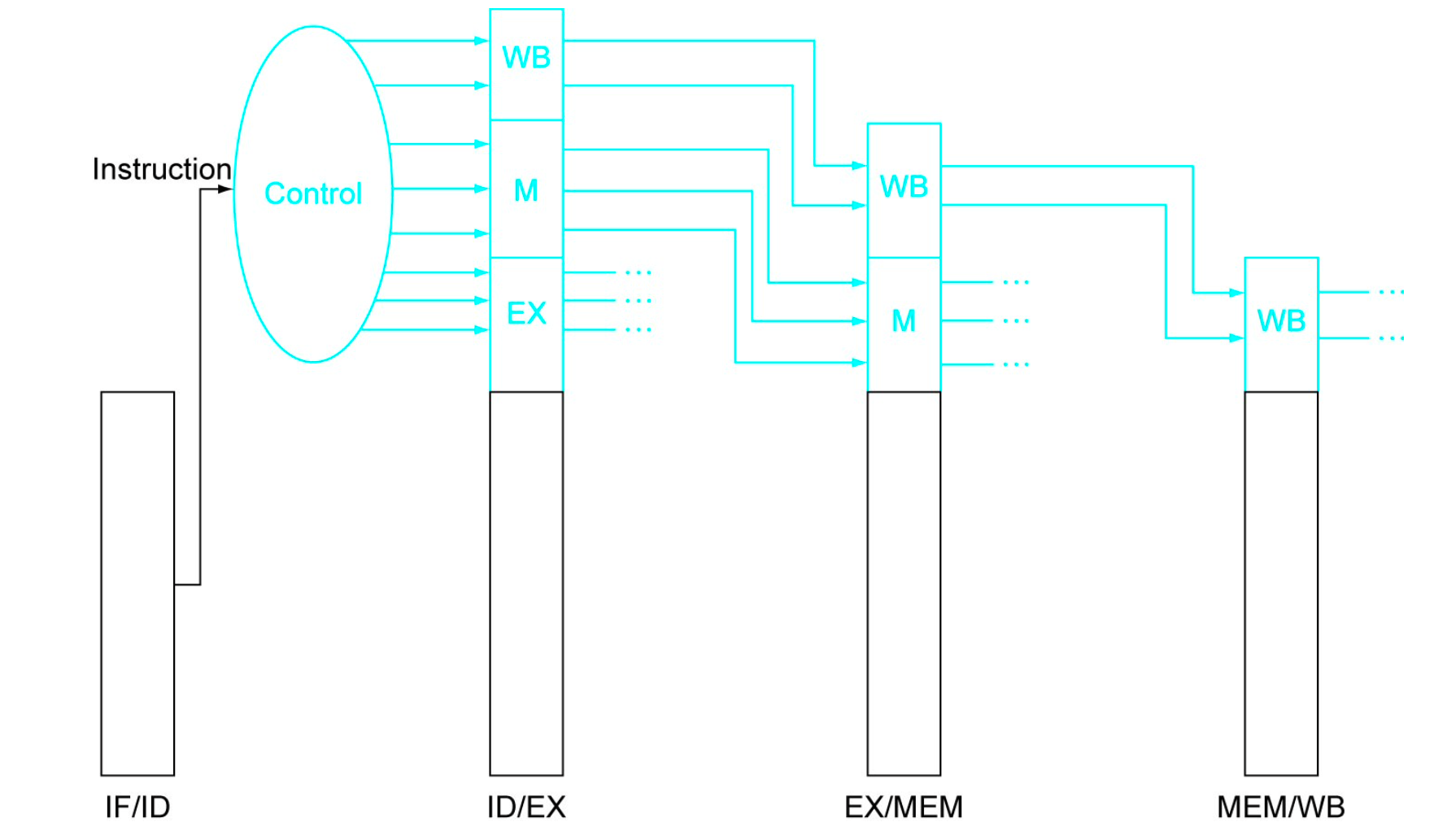
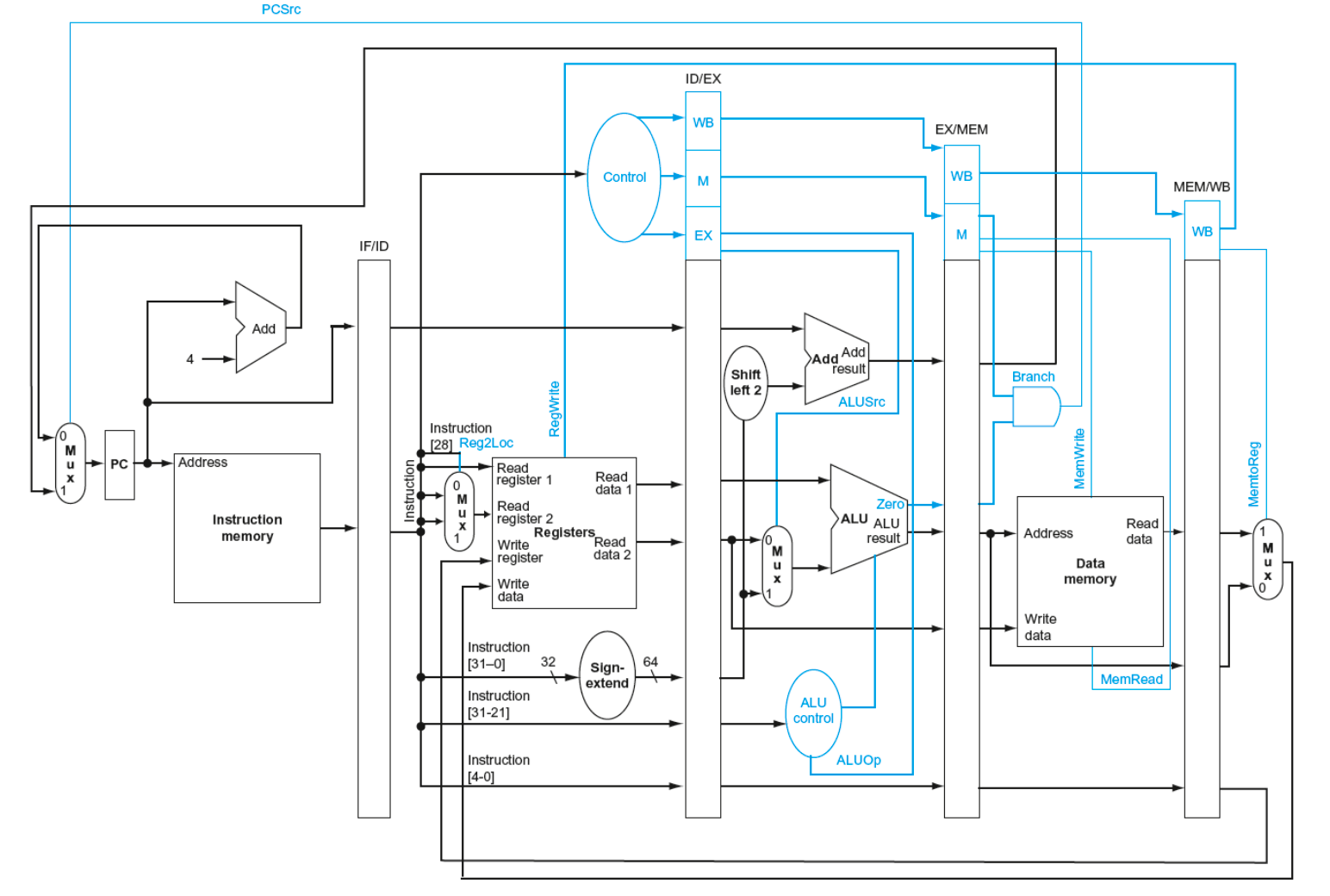
- In the wild, chips use distributed controllers but it is simpler to just think of a single one
Digital Logic Addition
- Modeled using Finite State Automata
- Implementation Options
- Hard-wired control
- Realized as combinational logic
- Advantage: Fast
- Drawback: Not flexible
- Microprogramming
- Behavior can be changed through memory override
- Advantage: Flexible
- Drawback: Slow