Diodes
Active component capable of controlling the current flow
How it works
- Can either create a depletion region or a conduction region in the center depending on the voltages on either end
- Forward bias → allows flow
- Reverse bias → prevents flow
- Forward bias
- Anode: Positive
- Cathode: Negative
Behavior
Ideal
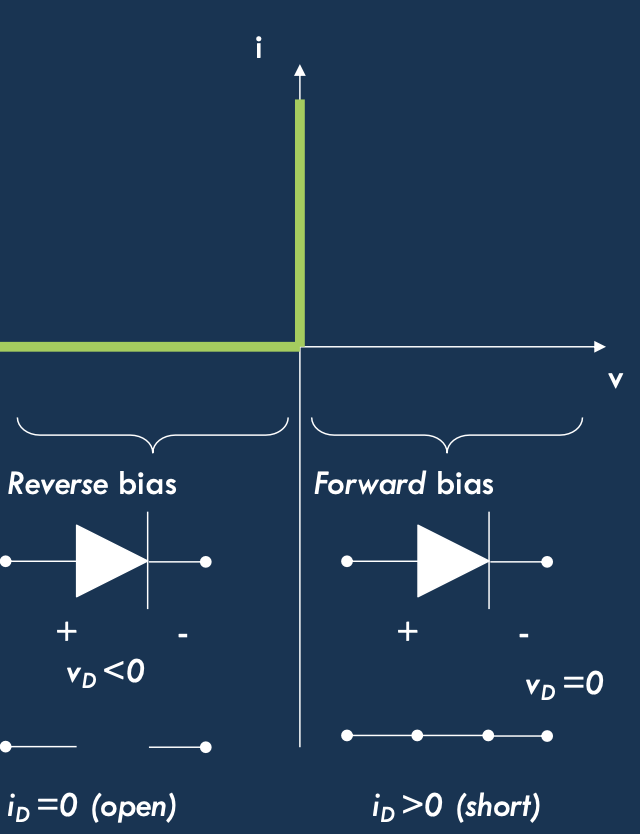
- Non linear over large scale
- Reverse bias → open
- Forward bias → short
Real World
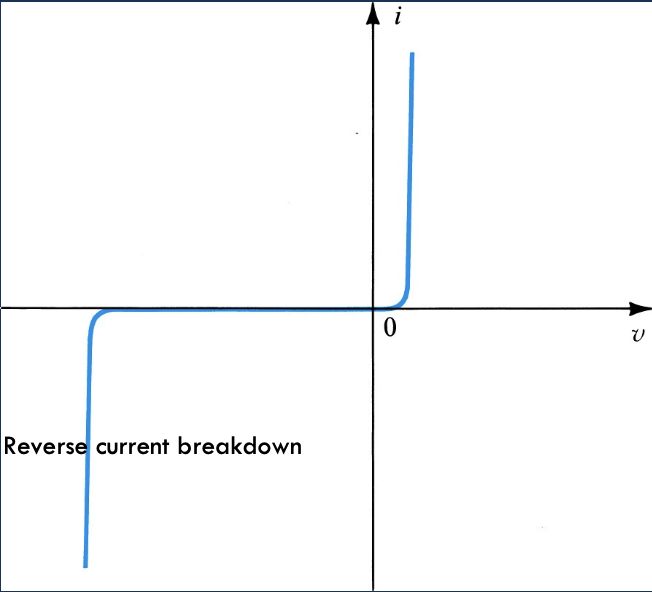
- = saturation current
- = thermal voltage
Constant voltage drop model:

Types
- Light Emitting Diode
- Photodiode (conducts when light hits the component)
Applications
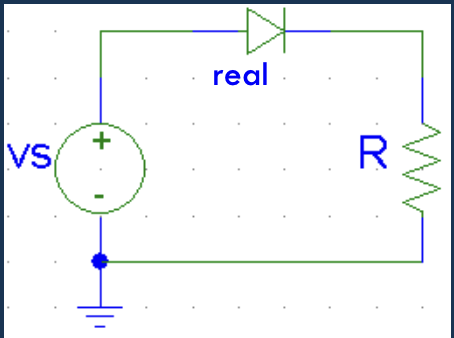
Rectifier
- A diode after a voltage source will prevent a waveform from going negative
- A key component in regulated power supplies
- Half wave
- Replaces negative values with 0
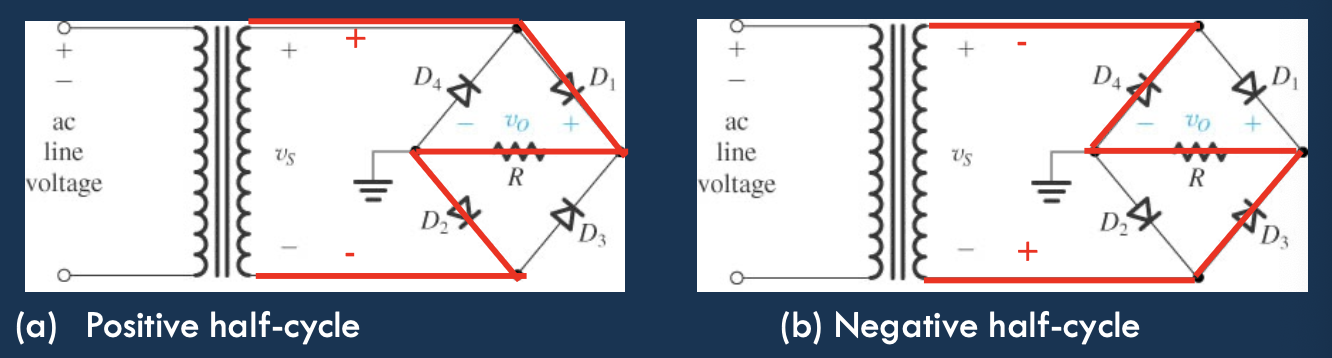
- Full Wave
- Replaces negative values with their absolute value
- Peak
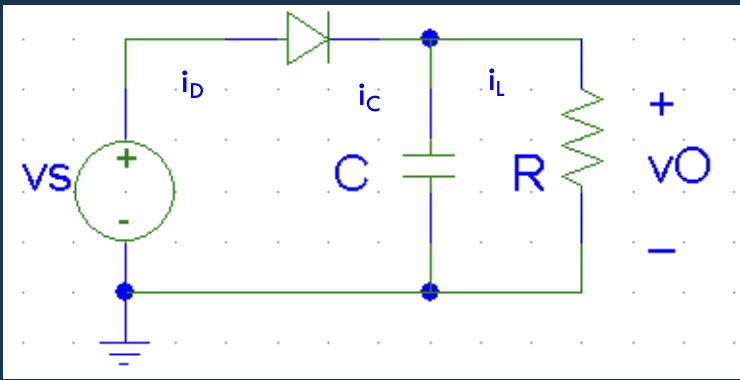
- Diode turns off at peak then C discharges through R
- Signal hovers approximately around the peak of the signal
Voltage Regulator
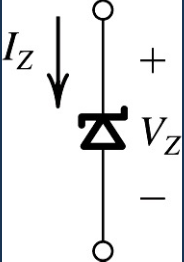
- Uses Zener Diodes
- Define and with opposite polarity
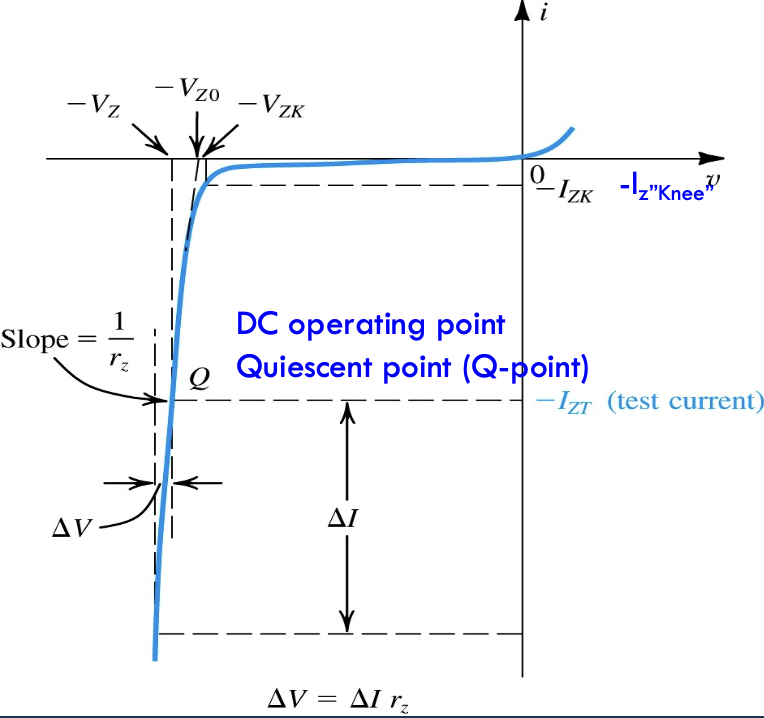
- Define and with opposite polarity