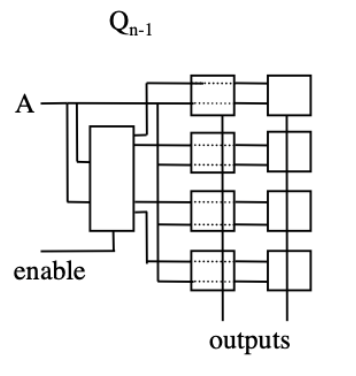
Read Only Memory (ROM)
- Nonvolatile memory
- Can be read from but not written to
- Uses
- Store software for general purpose processor
- Store constant data needed by system
- Implement combinational circuit as lookup table
Implementation
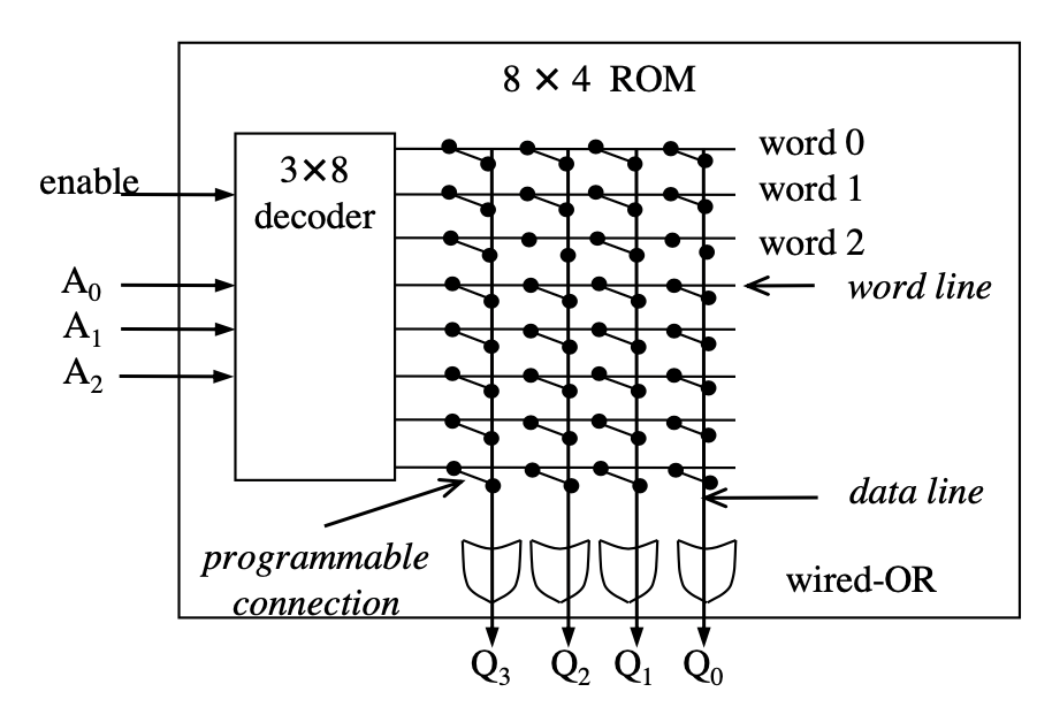
- Programmed by only connecting select programmable connections
Types
Mask-programmed
- Connected programmed at fabrication
- Shines a light on a set of masks, to etch circuit onto silicon
- Lowest write ability (only once)
- Highest storage performance (bits never changed unless damaged)
- Typically used for final designs of high-volume systems
One Time Programmable (OTP)
- Connections programmed after manufacture by user
- User provides file of desired contents of ROM
- each programmable connection is a fuse
- ROM programmer blows fuses for connections that should not exist
- Very low write ability (typically only once)
- Very high storage performance (would not change unless reconnected to programmer)
- Often used in final products
Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM)
- Programmable component is a MOS transistor
- Transistor has floating gate surrounded by an insulator
- Write 1: Negative charges form channel between source and drain
- Write 0: Large positive voltage at gate causes negative charges to move out of channel and get trapped in floating gate
- Erase: Shining UV rays on surface of floating gate causes negative charges to return to channel from floating gate
- Better write ability (can be reprogrammed thousands of times)
- Reduced storage permanence (lasts about 10 years but is susceptible to radiation and electrical noise)
- Typically used during design development
Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM)
- Programmed and erased electronically
- Typically by using a higher than normal voltage
- Can program and erase individual words
- Better write ability
- Similar storage to EPROM (about 10 years)
- Far more convenient than EPROM but more expensive
Flash
- Fast erase
- Large blocks of memory erased as once, rather than once word at a time
- Blocks typically several thousand bytes large
- Writes to single words may be slower
- Entire block must be read, modified, and then written back
- Used with embedded systems storing large data items in nonvolatile memory
- Extension of EEPROM
- Same floating gate principle
- Same write ability and storage permanence
Composing
- Parallel
- Increases word size
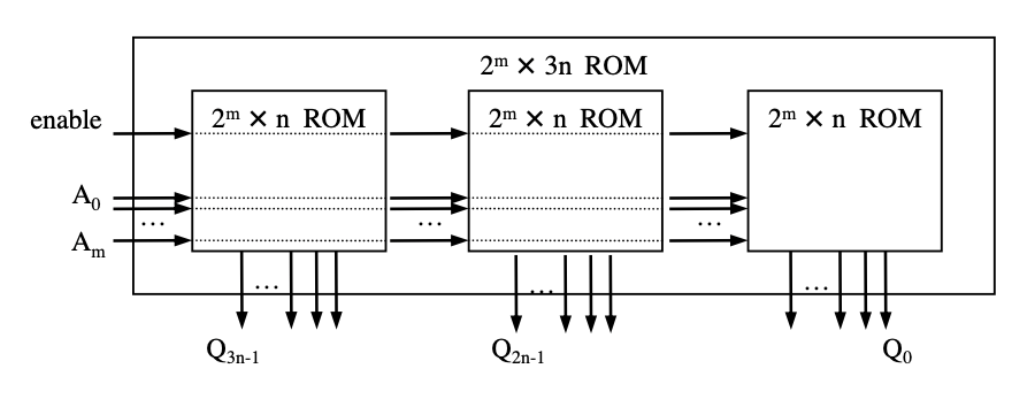
- Serial
- Increases number of words
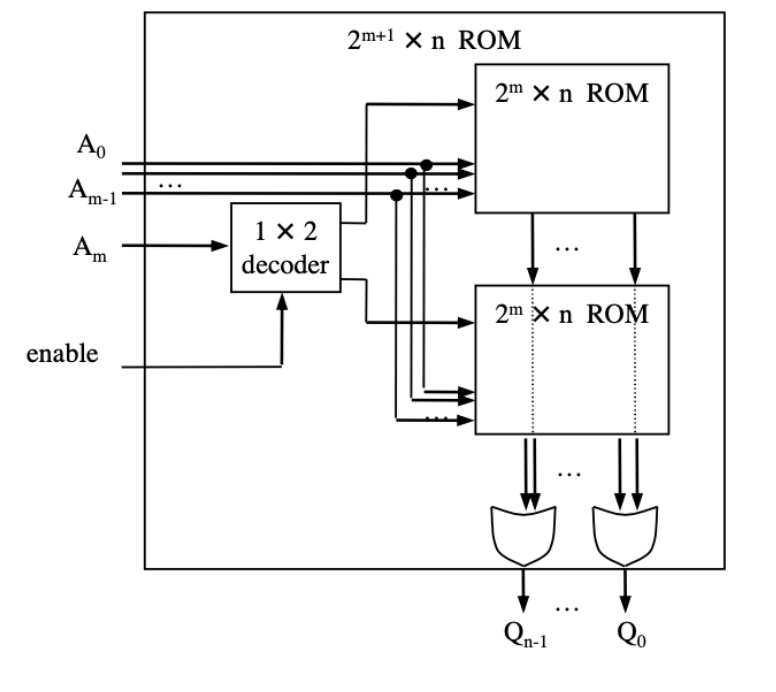
- Hybrid