Processors
Domain Specific
- Can do one thing
- Ex: matrix multiplication for machine learning
- Design Flow for Domain Specific
- Data Path
- Identify the components of the circuits
- Define the connections among the various units
- Define operations: for each method, 1 control signal
- Define condition: for each status signal, 1 status signal
- Controller
- Define 1 state for each sequential step
- For each state: define next and control signals
- Implement as hardwired or microprogrammed
- In practice, this is semi-automated
Von Neuman Architecture
- The data path has many different functions that can be switched between by the control
- Instructions are how we tell it what to do
- Max flexibility, min performance
- Structure
- Computer consists of processor + memory + in/output
- Memory consists of fixed length words (data and instructions)
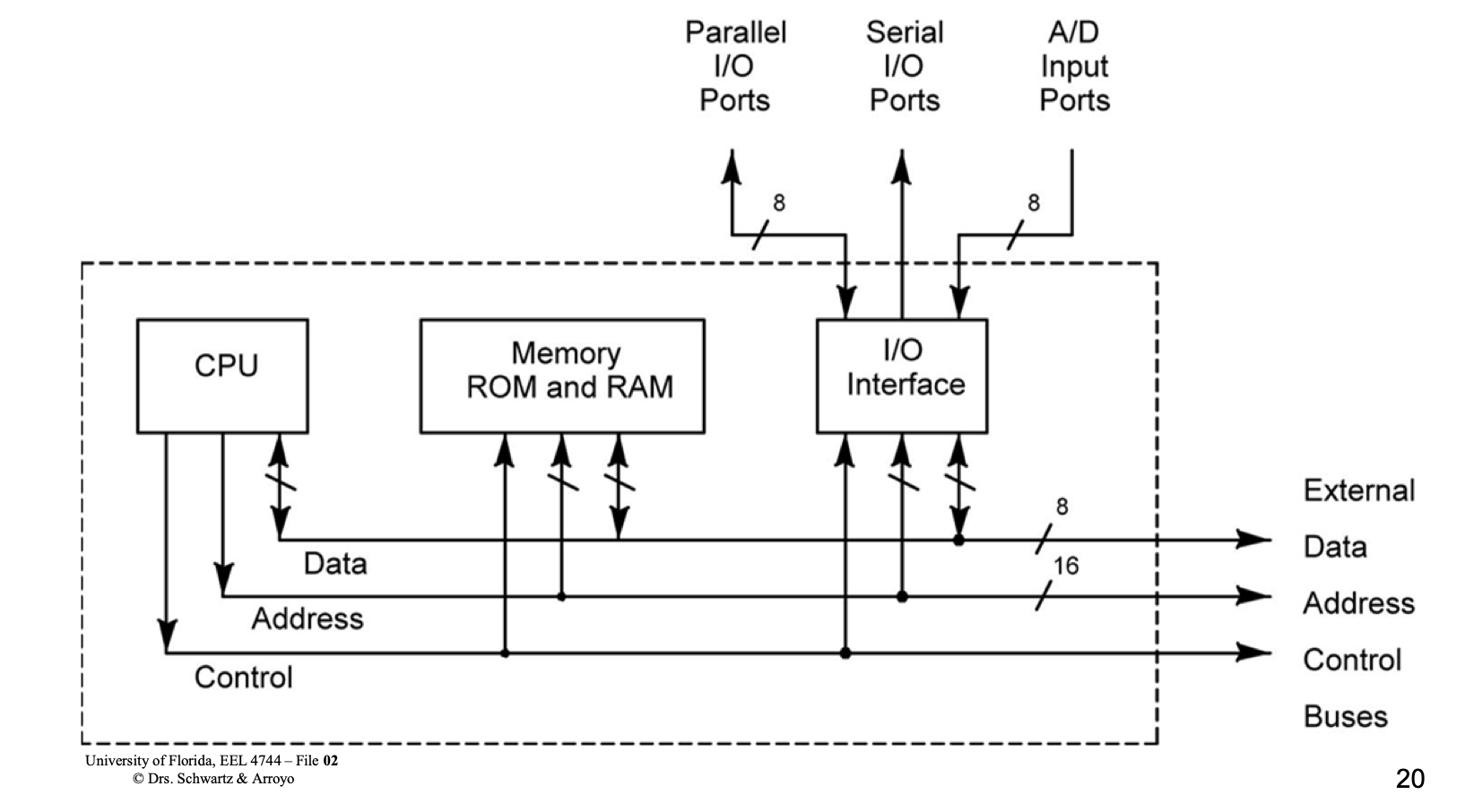
- Processor
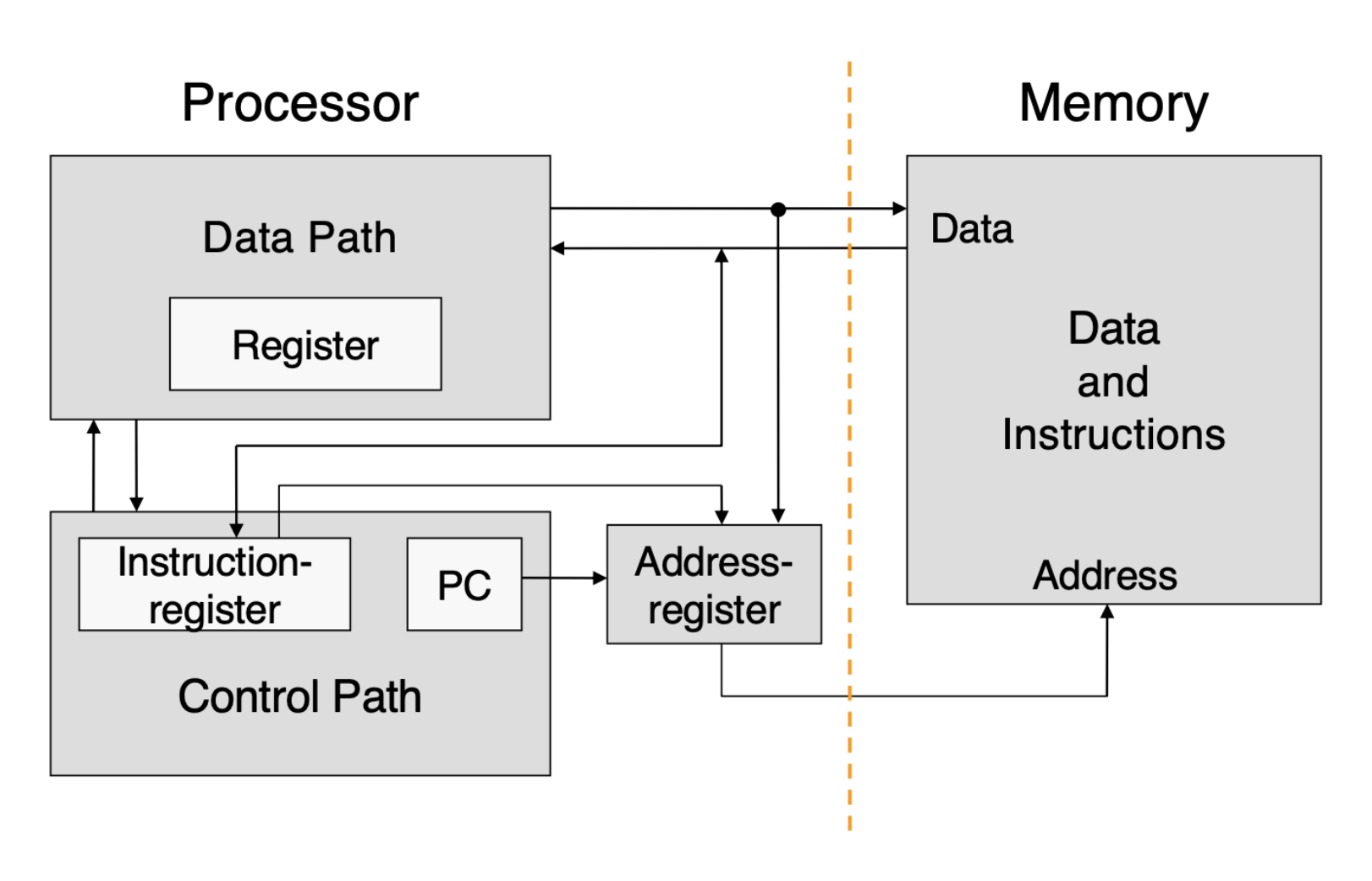
- Processor consists of data path and control path
- Together they make the CPU
- Program counter stores the memory address of the next instruction
- Registers in the data path improves performance
- Processor Cycle
- Instruction fetch
- Decode
- Read operand
- Execute
- Write back
- Clock is longest path from flip flop to flip flop
Harvard Architecture
- Von Neumann but program and data memory were stored separately
- Not used anymore because it does not work with Pipelining

