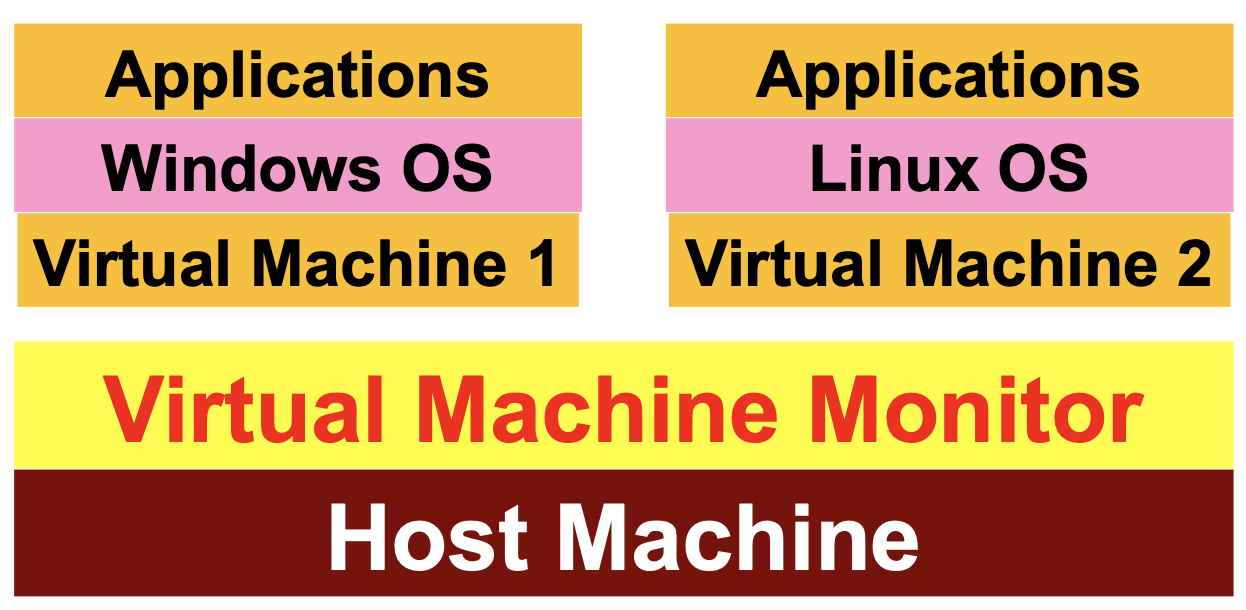
Virtual Machines
- Separates the hardware interface from the OS
- the OS still thinks it is using the hardware directly
Overhead
- Depends on the workload
- User-level processor-bound programs have zero overhead
- Because OS is rarely invoked
- I/O intensive → OS intensive
- Executes many system calls
- Can result in high overhead
- I/O intensive is also I/O bound
- Low processor utilization since waiting for I/O
- Processor virtualization can be hidden because something else is slower
Uses
- Increased Security
- Takes a portion of the operating system that provides hardware security and separates it
- Operating systems aren’t perfect, so they can’t always protect you
- Allows for increased scrutiny on security critical components
- Managing software
- Provide an abstraction that can run the complete SW stack
- Can also run old OSs or beta OSs
- Managing Hardware
- Allows separate SW stacks to run independently yet share HW
- A single server can be used my multiple clients isolated
