Lists
Properties
- Ordered collection of data
- Elements have some position
- Linear structure
- Can have some size or grow/shrink
- No limit on nature of elements
Characteristics
- Data
- Items
- Number of items (size)
- Capacity
- Operations
- Read/Write and element
- Add/Remove and element
- Find an element
- Count
- Traverse the list
Types
C++ Standard Template Library
- Array: Fixed size array
- Vector: Dynamic size array
- Forward_list: Single linked list
- List: Doubly linked list
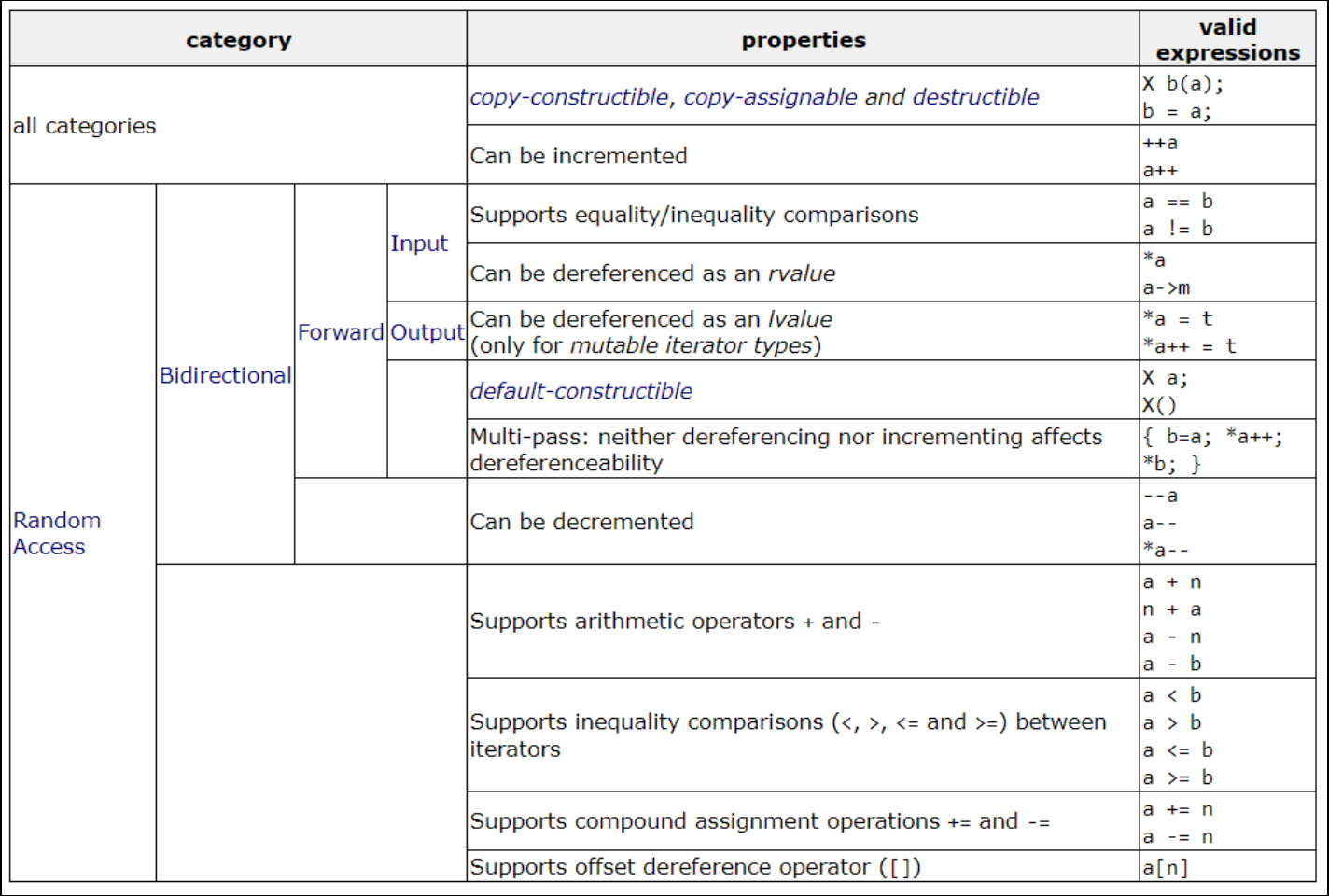
Iterators
Variables to keep track of where we are in a data set
Example Exam Question
Merge Two Sorted Lists of Integers
given ListA, ListB both sorted
create mergedList
place iterA at the head of list A, iterB at the head of list B
itemA is item iterA is pointing to and itemB is item iterB is pointing to
// add elements to new list (sorted) until one of them runs out
while iterA is not at end of ListA and iterB is not at end of ListB
if itemA == itemB
make a copy of itemA and add it to mergedList
move iterA and iterB forward
else if itemA < itemB
make a copy of itemA and add it to mergedList
move iterA forward
else
make a copy of itemB and add it to mergedList
move iterB forward
// add remaning elements from the remaining list
while iterA is not at end of list
make a copy of itemA and add it to mergedList
move iterA forward
while iterB is not at end of list
make a copy of itemB and add it to mergedList
move iterB forward
Slow Pointer, Fast Pointer
- Can have multiple pointers moving across your linked list at different rates, so when one hits the end you know the percentage through the list the others are
- Helpful if you don’t know the end of your linked list