Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits
Simplification for circuits with a port (two nodes) that is connected to a load
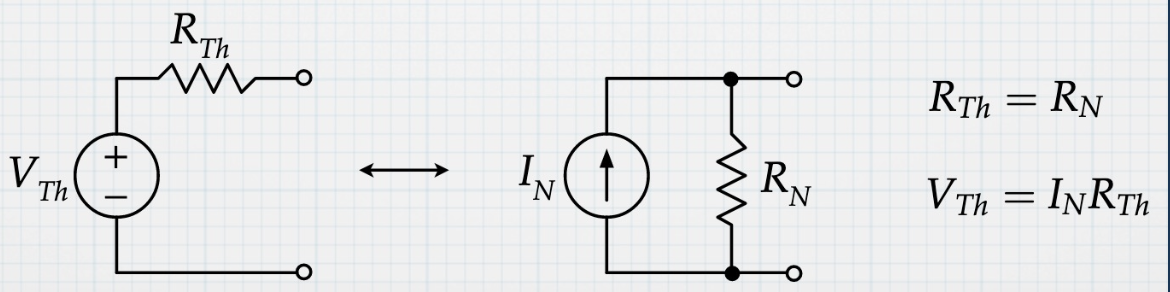
Thevenin
Simplified down to one voltage source () in series with one resistor ()
Finding
- In practice
- Disconnect the load
- measure the open circuit voltage,
- measure the short-circuit current,
- solve for
- When only independent
- Disconnect the load
- Calculate the open circuit voltage,
- measure the short-circuit current,
- Either
- Solve for
- Deactivate all the independent sources and solve for through port AB, =
- When only dependent
- Disconnect the load
- =
- Connect a known test source (current, or voltage, ) — use 1 for those test values
- Solve for the corresponding voltage, or current, at port
- Independent and Dependent Sources
- Disconnect the load
- Calculate the open circuit voltage,
- Calculate the short-circuit current,
- Optionally: Deactivate independent sources and connect a known test source at the load terminals and solve for the corresponding voltage
- Solve for
Maximum Power Transferred to Load
Power is maximized when so
Norton
Simplified down to one current source in parallel with one resistor
From Thevenin, use a Source Transformation