RL and RC Circuits
1st order transient response
Response Types
- Natural Response
- No sources, storage element has been energized and is supplying power
- Fully charged at
- Step Response
- Storage element is energized with a time constant dependent on the circuit
- Not fully charged at
- Switched Circuit Response
- Charges until given time and then switches to discharging
- Unbounded Response
- When Thevenin equivalent resistance has an unbounded value
- Keeps charging until the component breaks down
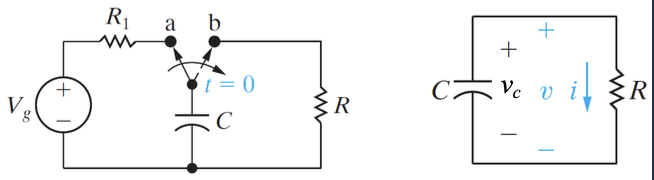
RC Circuits
- Resistors and Capacitors
- Time constant:
- Natural Response
- Step Response
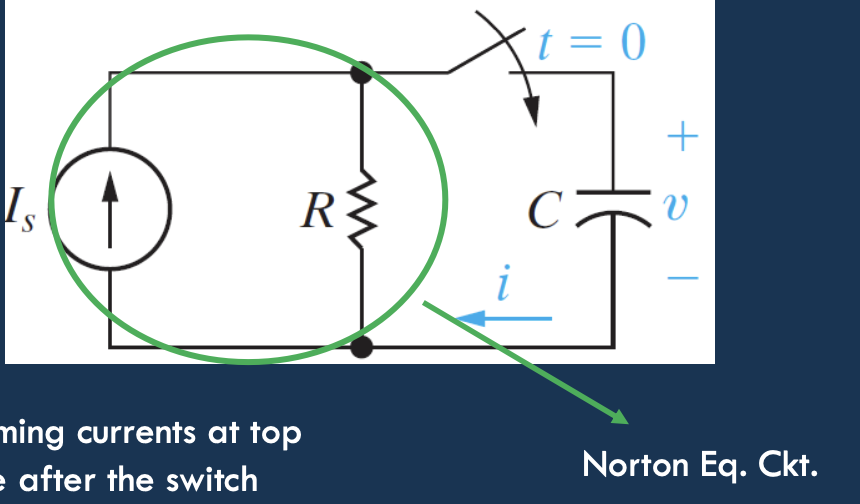
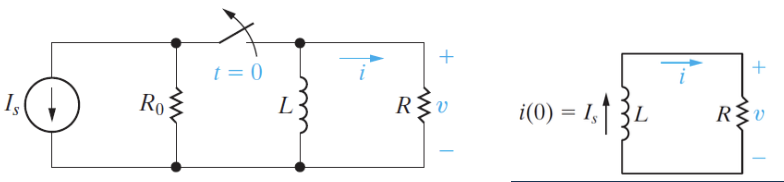
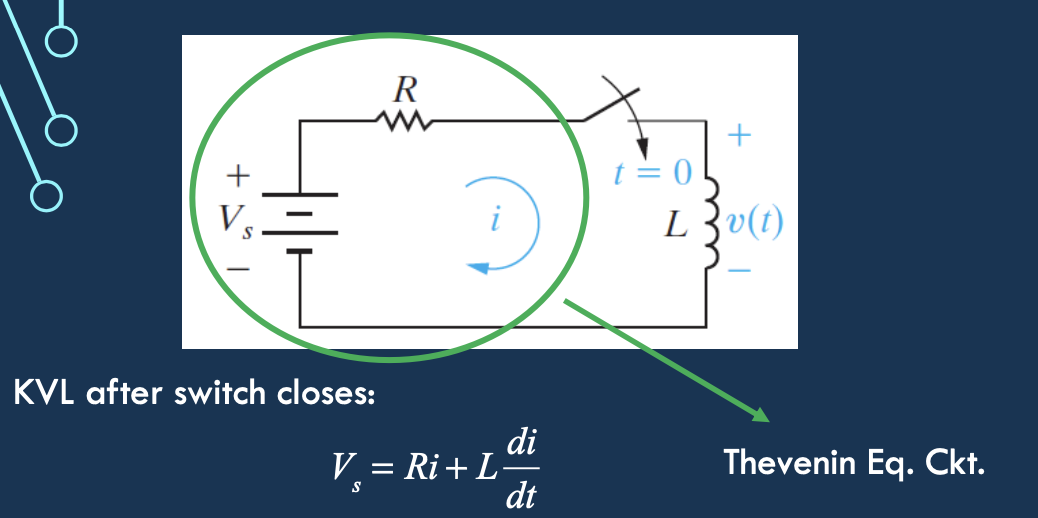
RL Circuit
RLC Circuit
- Resistors and Inductors and Capacitors
- Analogous to a mass (inductor), spring (capacitor), and damper (resistor)
- Results
- Under damped: moves quickly to equilibrium but will oscillate about the equilibrium as it does so (oscillations happen at the resonant frequency )
- Over damped: Moves slowly toward equilibrium
- Critically damped: moves as quickly as possible toward equilibrium without oscillation about the equilibrium
- Natural Response
- Characteristic roots
- Neper frequency:
- Resonant radian frequency:
- Possibilities
- over damped
- under damped
- critically damped
- Transient Responses
- Parallel RLC
- Natural → Voltage across the capacitor (same as others)
- Step → Current through the inductor
- Series RLC
- Natural → Current through the inductor (same as others)
- Step Response → Voltage across the capacitor
- Parallel RLC